Example models including higher order kinematic components
This notebook shows the user how to create a mock galaxy with higher order kinematic components such as planar and bar inflows.
Each model considered here includes the following components:
Disk + Bulge
NFW halo
Constant velocity dispersion
And, for the non-fiducial cases:
A non-circular, higher-order kinematic component
The structure of the notebook is the following:
Setup steps
Fiducial model
Example 1: Uniform planar inflow
Example 2: Uniform bar inflow
1) Setup steps
Import modules
from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals)
import copy
import numpy as np
import astropy.units as u
import astropy.io.fits as fits
from dysmalpy import galaxy, models, instrument, data_classes, \
parameters, observation, plotting
INFO:numexpr.utils:Note: NumExpr detected 10 cores but "NUMEXPR_MAX_THREADS" not set, so enforcing safe limit of 8.
INFO:numexpr.utils:NumExpr defaulting to 8 threads.
Setup notebook
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi']= 100
mpl.rc("savefig", dpi=300)
Import functions to tie scale height relative to effective radius, and the halo mass to the \(\boldsymbol{f_{DM}}\) value
from dysmalpy.fitting_wrappers.tied_functions import tie_sigz_reff, tie_lmvirial_to_fdm
Specify some settings for the plot contours
kwargs_contour = {'lw_cont': 0.75,
'delta_cont_v': 50.,
'delta_cont_disp': 25.,
'delta_cont_flux': 50.,
'delta_cont_v_minor': 10.,
'delta_cont_disp_minor': 5.,
'delta_cont_flux_minor': 10.,
'lw_cont_minor': 0.2,
'colors_cont_minor': 'black',
'delta_cont_flux_minor_resid': 0.2,
'delta_cont_disp_minor_resid': 1.,
'lw_cont_minor_resid': 0.15,
'ls_cont_minor_resid': ':',
'colors_cont_minor_resid': 'grey',
'max_residual': 100.}
Script to help with creating galaxy instances
def make_gal(name=None, hiord=None):
gal = galaxy.Galaxy(z=z, name=name)
mod_set = models.ModelSet()
obs = observation.Observation(name='mock', tracer='line')
obs.fit_options.fit_flux = True
obs.mod_options.oversample = 3
### Add all model components to ModelSet
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(bary), light=True)
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(halo))
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(disp_prof))
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(zheight_prof))
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(geom))
if hiord is not None:
mod_set.add_component(copy.deepcopy(hiord), light=False)
### Set kinematic options for calculating velocity profile
mod_set.kinematic_options.adiabatic_contract = False
mod_set.kinematic_options.pressure_support = True
### Add the model set, instrument to the Galaxy / observation
gal.model = copy.deepcopy(mod_set)
obs.instrument = copy.deepcopy(inst)
gal.add_observation(obs)
return gal
2) Fiducial model
# Redshift:
z = 2.
Baryonic component: Combined Disk+Bulge
total_mass = 10.5 # M_sun
bt = 0.3 # Bulge-Total ratio
r_eff_disk = 4.0 # kpc
n_disk = 1.0
invq_disk = 5.0
r_eff_bulge = 1.0 # kpc
n_bulge = 4.0
invq_bulge = 1.0
noord_flat = True # Switch for applying Noordermeer flattening
# Fix components
bary_fixed = {'total_mass': False,
'r_eff_disk': False,
'n_disk': True,
'r_eff_bulge': True,
'n_bulge': True,
'bt': False}
# Set bounds
bary_bounds = {'total_mass': (10, 13),
'r_eff_disk': (1.0, 30.0),
'n_disk': (1, 8),
'r_eff_bulge': (1, 5),
'n_bulge': (1, 8),
'bt': (0, 1)}
bary = models.DiskBulge(total_mass=total_mass, bt=bt,
r_eff_disk=r_eff_disk, n_disk=n_disk,
invq_disk=invq_disk,
r_eff_bulge=r_eff_bulge, n_bulge=n_bulge,
invq_bulge=invq_bulge,
noord_flat=noord_flat,
name='disk+bulge',
fixed=bary_fixed, bounds=bary_bounds)
bary.r_eff_disk.prior = parameters.BoundedGaussianPrior(center=5.0, stddev=1.0)
Halo component
mvirial = -99
conc = 5.0
fdm = 0.5
halo_fixed = {'mvirial': False,
'conc': True,
'fdm': False}
halo_bounds = {'mvirial': (10, 13),
'conc': (1, 20),
'fdm': (0, 1)}
halo = models.NFW(mvirial=mvirial, conc=conc, fdm=fdm, z=z,
fixed=halo_fixed, bounds=halo_bounds, name='halo')
halo.mvirial.tied = tie_lmvirial_to_fdm
# The tied component must have "fixed=False", and then a specified tied function
Dispersion profile
sigma0 = 39. # km/s
disp_fixed = {'sigma0': False}
disp_bounds = {'sigma0': (5, 300)}
disp_prof = models.DispersionConst(sigma0=sigma0, fixed=disp_fixed,
bounds=disp_bounds, name='dispprof',
tracer='line')
Light z-height profile
sigmaz = 0.9 # kpc
zheight_fixed = {'sigmaz': False}
zheight_prof = models.ZHeightGauss(sigmaz=sigmaz, name='zheightgaus',
fixed=zheight_fixed)
zheight_prof.sigmaz.tied = tie_sigz_reff
# The tied component must have "fixed=False", and then a specified tied function
Geometry
inc = 62. # degrees
pa = 142. # degrees, blue-shifted side CCW from north
xshift = 0 # pixels from center
yshift = 0 # pixels from center
geom_fixed = {'inc': False,
'pa': True,
'xshift': True,
'yshift': True}
geom_bounds = {'inc': (0, 90),
'pa': (90, 180),
'xshift': (0, 4),
'yshift': (-10, -4)}
geom = models.Geometry(inc=inc, pa=pa, xshift=xshift, yshift=yshift,
fixed=geom_fixed, bounds=geom_bounds, name='geom',
obs_name='mock')
Set up the instrument
inst = instrument.Instrument()
inst.ndim = 2
beamsize = 0.55*u.arcsec # FWHM of beam
sig_inst = 45*u.km/u.s # Instrumental spectral resolution
beam = instrument.GaussianBeam(major=beamsize)
lsf = instrument.LSF(sig_inst)
inst.beam = beam
inst.lsf = lsf
inst.pixscale = 0.125*u.arcsec # arcsec/pixel
inst.fov = [33, 33] # (nx, ny) pixels
inst.spec_type = 'velocity' # 'velocity' or 'wavelength'
inst.spec_step = 10*u.km/u.s # Spectral step
inst.spec_start = -1000*u.km/u.s # Starting value of spectrum
inst.nspec = 201 # Number of spectral pixels
# Set the beam kernel so it doesn't have to be calculated every step
inst.set_beam_kernel()
inst.set_lsf_kernel()
Setup the galaxy and model set
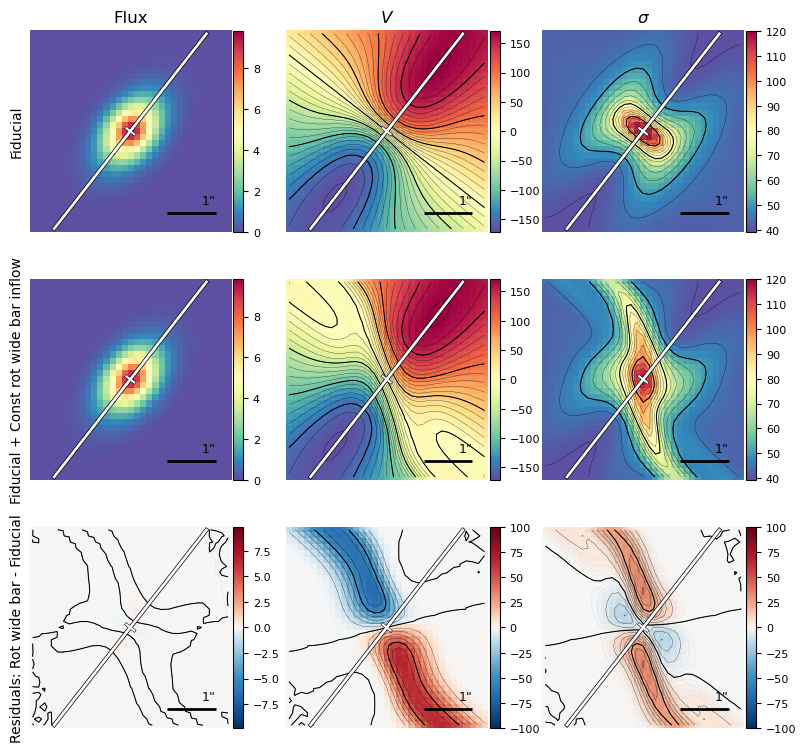
gal = make_gal(name='galaxy')
Create 2D model
gal.create_model_data()
plotting.plot_model_2D(gal, inst_corr=True, ruler_loc='lowerright')
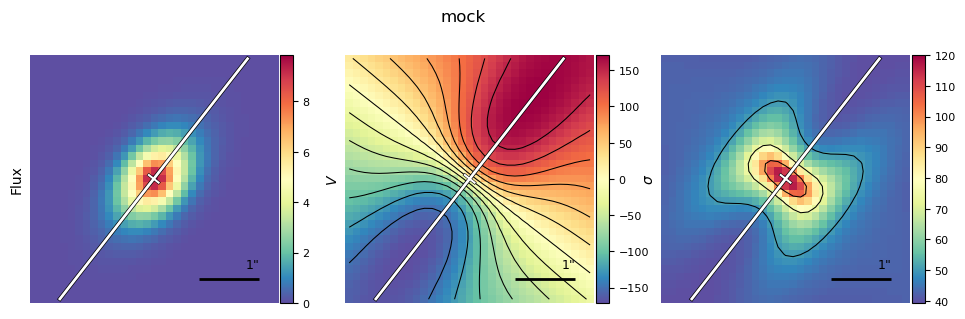
Example 1: Uniform planar inflow
Define the higher-order kinematic component
vr = -90.
uniform_planar_inflow = models.PlanarUniformRadialFlow(vr=vr,
name='uniform_planar_inflow')
Setup the galaxy and model set
gal_planar_inflow = make_gal(name='galaxy_planar_uniform_inflow',
hiord=uniform_planar_inflow)
Create 2D model and compare to fiducial
gal_planar_inflow.create_model_data()
plotting.plot_model_comparison_2D(obs1=gal.observations['mock'],
obs2=gal_planar_inflow.observations['mock'],
model1=gal.model, model2=gal_planar_inflow.model,
label_gal1='Fiducial',
label_gal2='Fiducial + Const planar radial inflow',
label_residuals='Residuals: Inflow - Fiducial',
show_contours=True, **kwargs_contour)
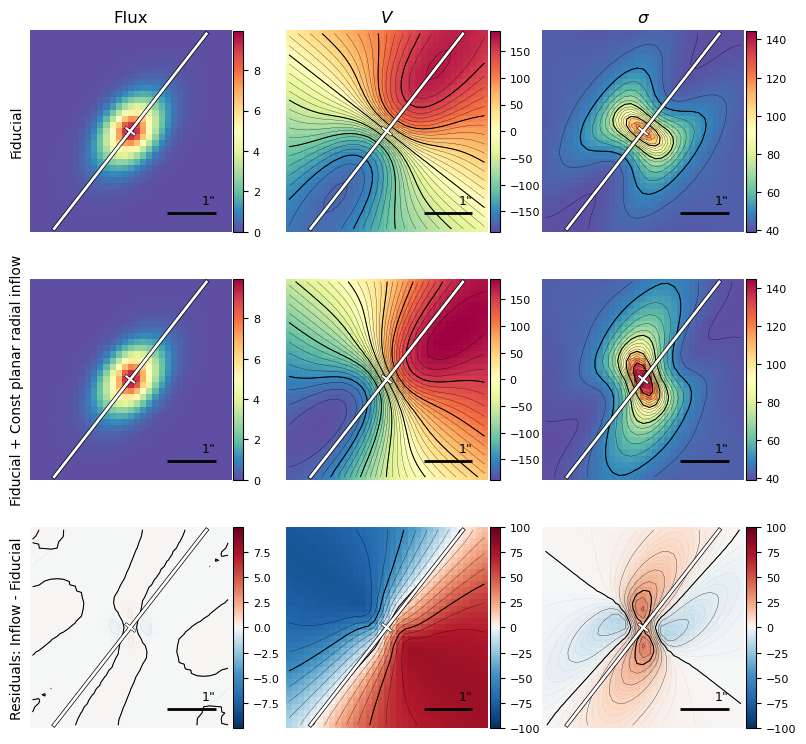
Example 2: Uniform bar inflow
Define the higher-order kinematic components
# Narrow bar
vbar = -90.
bar_width = 2.
phi = 90.
bar = models.UniformBarFlow(vbar=vbar, bar_width=bar_width,
phi=phi, name='bar')
# Wide bar
vbar = -90.
bar_width = 5.
phi = 90.
bar_wide = models.UniformBarFlow(vbar=vbar, bar_width=bar_width,
phi=phi, name='bar_wide')
# Wide bar, rotated
vbar = -90.
bar_width = 5.
phi = 70.
bar_wide_rot = models.UniformBarFlow(vbar=vbar, bar_width=bar_width,
phi=phi, name='bar_wide_rot')
Setup the galaxy and model set
gal_bar = make_gal(name='galaxy_bar', hiord=bar)
gal_wide_bar = make_gal(name='galaxy_wide_bar', hiord=bar_wide)
gal_wide_bar_rot = make_gal(name='galaxy_wide_bar_rot', hiord=bar_wide_rot)
Create 2D model and compare to fiducial
gal_bar.create_model_data()
gal_wide_bar.create_model_data()
gal_wide_bar_rot.create_model_data()
plotting.plot_model_comparison_2D(obs1=gal.observations['mock'],
obs2=gal_bar.observations['mock'],
model1=gal.model, model2=gal_bar.model,
label_gal1='Fiducial',
label_gal2='Fiducial + Const bar inflow',
label_residuals='Residuals: Bar - Fiducial',
show_contours=True, **kwargs_contour)
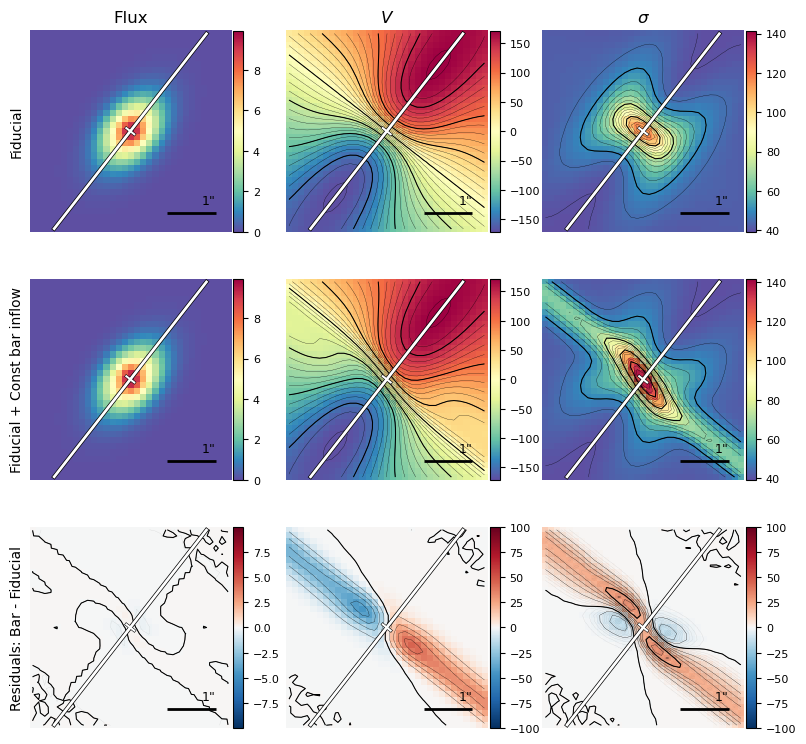
plotting.plot_model_comparison_2D(obs1=gal.observations['mock'],
obs2=gal_wide_bar.observations['mock'],
model1=gal.model, model2=gal_wide_bar.model,
label_gal1='Fiducial',
label_gal2='Fiducial + Const wide bar inflow',
label_residuals='Residuals: Wide bar - Fiducial',
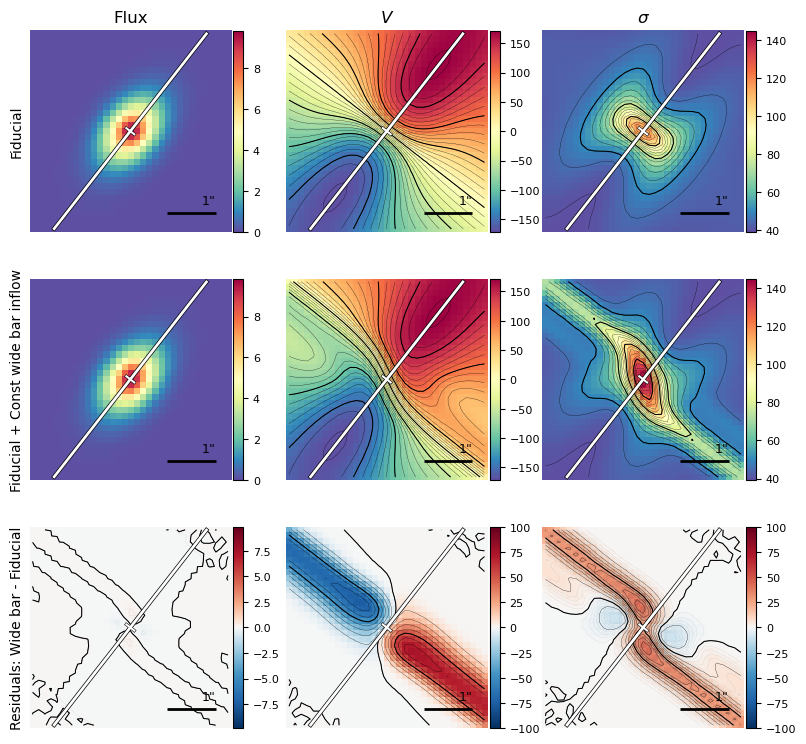
show_contours=True, **kwargs_contour)
plotting.plot_model_comparison_2D(obs1=gal.observations['mock'],
obs2=gal_wide_bar_rot.observations['mock'],
model1=gal.model, model2=gal_wide_bar_rot.model,
label_gal1='Fiducial',
label_gal2='Fiducial + Const rot wide bar inflow',
label_residuals='Residuals: Rot wide bar - Fiducial',
show_contours=True, **kwargs_contour)